IN THIS ARTICLE:
 AXIAL
AXIAL
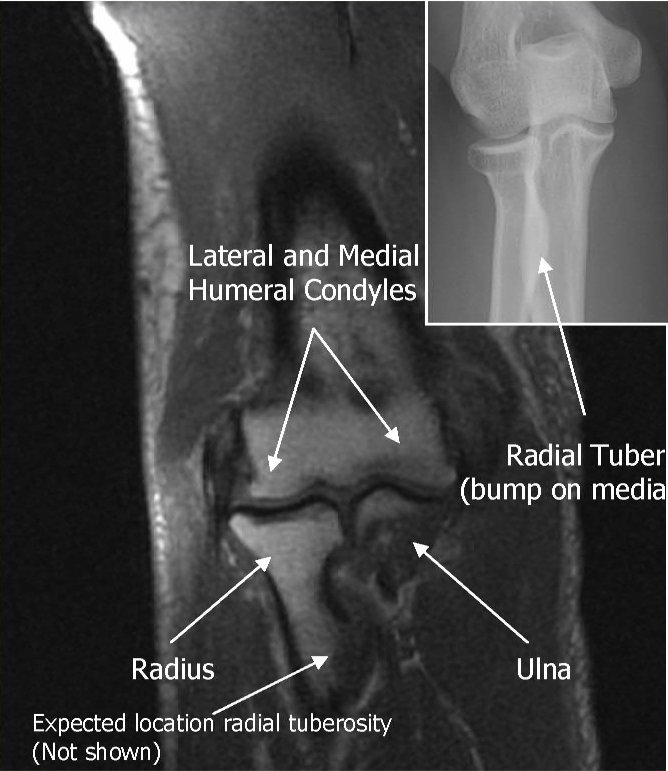
CORONAL REFERENCE LINE IN MRI PLANNING
SAGITAL REFERENCE LINE IN MRI PLANNING
 Photograph shows patient positioning for flexed abducted supinated view: patient is positioned prone on MRI table with elbow in flexed abducted supinated view position. Notice position of arm, flexed at elbow and abducted at shoulder with supinated forearm, thumb up.
Photograph shows patient positioning for flexed abducted supinated view: patient is positioned prone on MRI table with elbow in flexed abducted supinated view position. Notice position of arm, flexed at elbow and abducted at shoulder with supinated forearm, thumb up.
In general, it was preferable for the patient to lie prone for these views. The shoulder was abducted 180°, with the arm beside the head. The elbow was flexed to 90°, with the forearm supinated, thumb up, and a shoulder phased array coil was placed around the elbow . The position is referred to in this article as the flexed abducted supinated view, but usually in our practice it is termed the “FABS view,” meaning the flexed elbow with the shoulder abducted and the forearm in supination view.

Localizer MR image with lines shows slice positioning for flexed abducted supinated view. Notice sections, sagittal to long axis of body but coronal to anatomy at elbow. Ideal angulation is planned along distal biceps brachii tendon, but often, as here, this structure is not clearly visible on localizer images. In this case, sections nearly perpendicular to radius provide reasonable and reproducible imaging plane.
 Coronal T1
Coronal T1
Coronal T1 and PD fat suppressed sequence are well suited for evaluation of collateral ligament and common extensor/flexor tendon group patholgy as well as epicondylitis.
 COR PD FAT SAT
COR PD FAT SAT
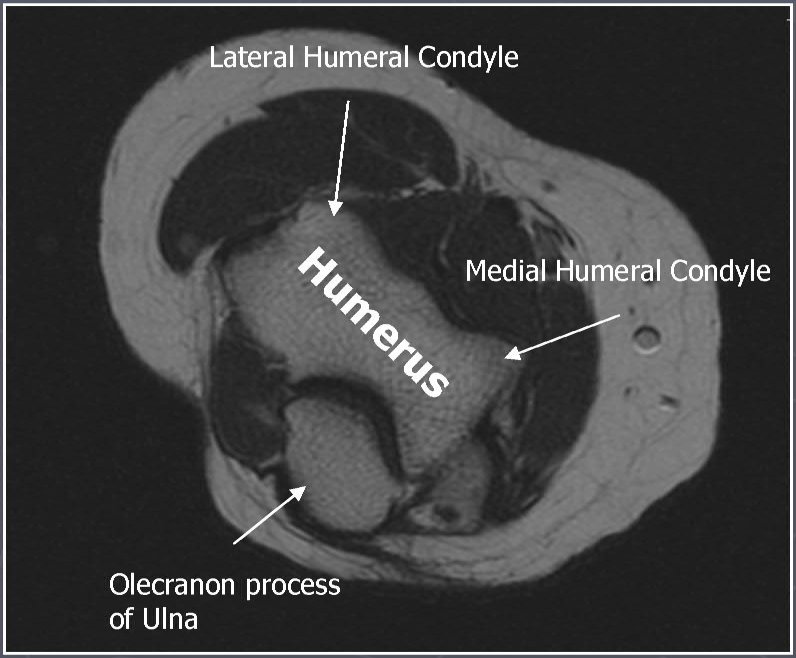
 AXIAL T1
AXIAL T1
Axial T1 and PD FSE fat suppressed sequences evaluate the tendons of the Biceps Brachii and Brachiallis muscles transversely as they insert onto the Radius and Ulna respectively. The distal Triceps tendon is also well evlauated in this plane.
 AXIAL PD FAT SAT
AXIAL PD FAT SAT
 T1 SAG
T1 SAG
Sagittal T1 and PD FSE fat sat sequences evaluate the tendons of the Biceps Brachii and Brachiallis muscles as they travel distally to instert onto the Radius and Ulna respectively. They also help evaluate the Radial head for radiographically occult fractures. The distal Triceps tendon is also well evlauated in this plane.
 PD FAT SAT SAG
PD FAT SAT SAG
 ELBOW ARTHROGRAM
ELBOW ARTHROGRAM
Coronal T1 fat saturated arthrogram is useful for evaluation of the collateral ligaments and cartilage surfaces.
READ MORE ABOUT:
MRI ELBOW PROTOCOL
- AXIAL REFERENCE LINE
- CORONAL REFERENCE LINE
- SAGITAL REFERENCE LINE
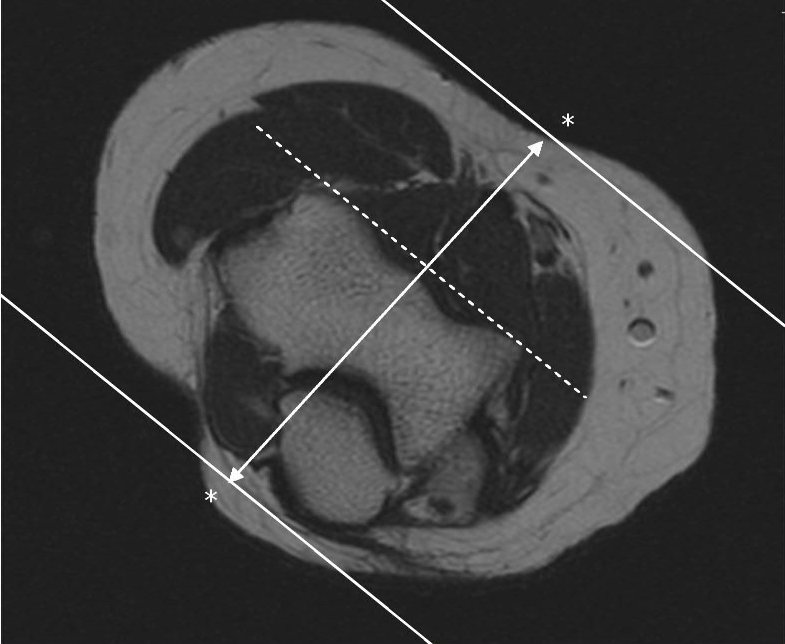
AXIAL REFERENCE LINE- Perpendicular to Coronal
Use COR to angle parallel to elbow joint (parallel to capitellum and trochlea),Cover from 1 slice distal to radial tuberosity up as far as the slices go. Parallel Sat Bands (above and below)
CORONAL REFERENCE LINE
Use axial LOC to angle parallel to anterior portions of the capitellum and
trochlea (or parallel to humeral epicondyles)
Use sagittal LOC to angle parallel to humerus/radius/ulnar plane, but
closer to plane of radius if minimally flexed (if markedly flexed elbow,
then angle between anterior humerus and the radius)
SAGITAL REFERENCE LINE
Perpendicular to both Coronal and Axial sequences,Cover 1 slice outside of both humeral epicondyles
AXIAL REFERENCE LINE IN MRI PLANNING
AXIAL REFERENCE LINES
CORONAL ELBOW REFERENCE LINES
FABS VIEW
In general, it was preferable for the patient to lie prone for these views. The shoulder was abducted 180°, with the arm beside the head. The elbow was flexed to 90°, with the forearm supinated, thumb up, and a shoulder phased array coil was placed around the elbow . The position is referred to in this article as the flexed abducted supinated view, but usually in our practice it is termed the “FABS view,” meaning the flexed elbow with the shoulder abducted and the forearm in supination view.
Localizer MR image with lines shows slice positioning for flexed abducted supinated view. Notice sections, sagittal to long axis of body but coronal to anatomy at elbow. Ideal angulation is planned along distal biceps brachii tendon, but often, as here, this structure is not clearly visible on localizer images. In this case, sections nearly perpendicular to radius provide reasonable and reproducible imaging plane.
Coronal T1 and PD fat suppressed sequence are well suited for evaluation of collateral ligament and common extensor/flexor tendon group patholgy as well as epicondylitis.
Axial T1 and PD FSE fat suppressed sequences evaluate the tendons of the Biceps Brachii and Brachiallis muscles transversely as they insert onto the Radius and Ulna respectively. The distal Triceps tendon is also well evlauated in this plane.
Sagittal T1 and PD FSE fat sat sequences evaluate the tendons of the Biceps Brachii and Brachiallis muscles as they travel distally to instert onto the Radius and Ulna respectively. They also help evaluate the Radial head for radiographically occult fractures. The distal Triceps tendon is also well evlauated in this plane.
Coronal T1 fat saturated arthrogram is useful for evaluation of the collateral ligaments and cartilage surfaces.
READ MORE ABOUT:
MRI ELBOW PROTOCOL